Contents
What is the Compression Ratio?
When we talk about the power output of the internal combustion engine, the researchers made a study to modify the factors affecting the power output of the IC engine, the configuration of an engine like CC which is decided after various research. Is the cylinder size affect the engine’s power output? What is the effect of cubic capacity on the engine’s output? What is the compression ratio?
The compression ratio (CR) of an IC engine is a ratio of the total volume of the combustion chamber to the volume left after complete compression-like clearance volume. Let us understand in simple words it is the ratio between the total volume of the combustion chamber which left when the piston is at BDC and volume let inside the combustion chamber when the piston moves to its TDC.
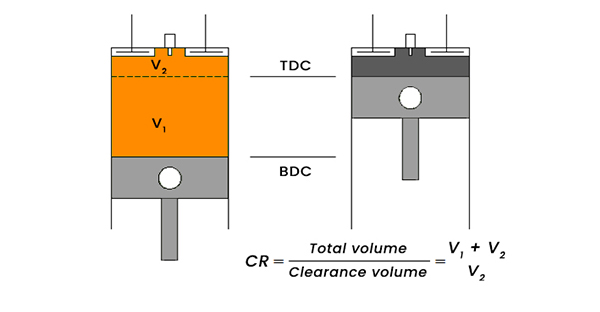
Let us take one example – For example, an engine having 1000cc total volume out of which 900cc is swept volume. The swept volume is covered by the piston when it moves from BDC to TDC. And has 100cc of clearance volume. It is the volume left inside the cylinder when the piston is reached to its TDC. So the compression ratio of the engine is 1000:100 or 10:1.
It is proved that the greater the compression ratio more the power output of the engine.
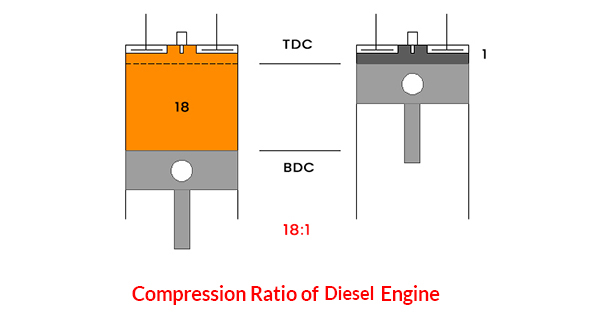
A compression ratio of the diesel engine is much higher than the petrol engine. The petrol engine has a compression ratio of 10:1 to 14:1. The diesel engine has a compression ratio of 18:1 to 23:1.
Read Also: What is Carburetor?Why Compression Ratio is important?
The compression ratio is very important as the design team has to determine while designing the engine. The compression ratio is selected according to the output need of the engine. And it directly affects the engine output and overall size of the engine.
For the diesel and petrol engine the CR is different which is explained below:
Petrol Engine
For the 4-stroke petrol engine has its own significance which are:
As we know in the petrol engine there is air-fuel mixture enters into combustion chamber during suction stroke and for proper mixing and for proper mixing and combustion of air-fuel mixture compression of mixture which require done by engine in its compression stroke and a good compression ratio of petrol engine is required for proper combustion of air-fuel mixture and in provides better thermal efficiency.
The pressure inside the cylinder increases in the compression stroke and it increases the temperature of an air-fuel mixture which leads to complete or proper combustion of fuel when spark plug produces spark which in turn provides better fuel economy and also prevents the engine from various defects like knocking.
The petrol engine having proper CR gives a balanced amount of speed and power.
The petrol engine comes with a 10:1 to 14:1 compression ratio depending upon the application and design requirement.
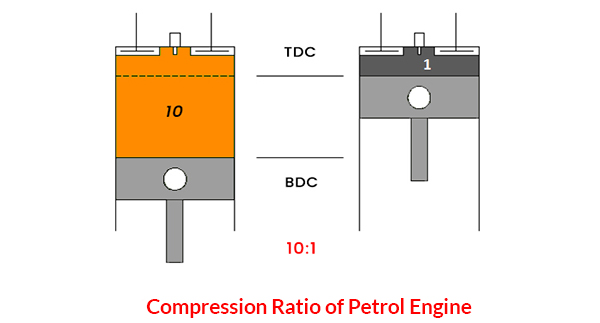
Diesel Engine
A diesel engine has greater significance in compression ratio like:
For the diesel engine, a high CR is required as diesel engines don’t have any spark plug and because of it, the combustion of fuel depends on compression of air provided by compression stroke of diesel cycle as the diesel engine is also known as compression ignition engine.
Diesel engine with high compression ratio provides the engine the compression and it provides high-pressure rise which is required to increase the temperature of the compressing air to extent of the autoignition temperature of the fuel that is to be sprayed by the fuel injectors which it turns provide complete or proper combustion of fuel.
As we know the diesel engine is used for high power output and it requires a high compression ratio. And higher the CR higher the thermal efficiency or work output.
Diesel engine with high CR has a high fuel economy. And due to the higher thermal efficiency provided by high compression combustion.
The diesel engine comes with higher CR and varies from 18:1 to 23:1 depends upon the application and design requirement.
CR Depends on which Design Criteria?
Stroke Length – Stroke Length of the engine is the distance between TDC and BDC of the engine cylinder or length of the combustion chamber. CR is depending on stroke length. The higher the stroke length the higher the CR.
Bore Diameter – The engine cylinder shape is cylindrical and the bore diameter of an engine is the diameter of the engine’s cylinder inside the piston is moving. CR of the engine is depending on bore diameter and as higher the bore diameter of the engine has higher the CR.
Square Engine – In this type of engine, the stroke length of the cylinder is equal to the bore diameter of the engine cylinder and gives a properly balanced power and speed output.
Attention
There is no engine in the world that is square practically. But the formula 1 engine is nearest to a square.
Number of Cylinder – The cylinder number also affects the CR of an engine and as the engine has a higher number of pistons provides a higher CR.
It is concluded that the bigger the size of the engine has a higher compression ratio than the small engine.
In the bigger size requirements of in-line engines with high CR, then the V-shape engines have come which provide a high CR with having a compact size of the engine.
So, this is the information about the Compression Ratio, engine compression ratio. If you find any information missing or mismatch let us know by comment.
Thank you for reading.