Contents
What is Stress Strain Curve?
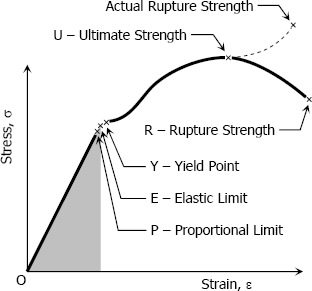
Take one metal piece and place it in a tension-compression-testing machine. In this test the axial load is increased gradually and the total elongation over the gauge length is measured of the load until the failure of the piece. With the cross-sectional area and length, the stress σ and strain ε can be obtained. Graph having stress σ on the y-axis and ε strain on the x-axis is known as stress strain diagram. The stress-strain curve is different for different materials. The below stress strain curve is for medium-carbon structural steel.
Read Also: Mechanical Properties of MaterialThe metallic materials are divided into ductile or brittle materials. Ductile materials have the large tensile strains up to point of rupture like the materials structural steel and aluminum. On the other side, brittle materials have small stains up to point of ruptures like cast iron and concrete.
Proportional Limit
At the proportional limit, the value of stress and strain remains proportional. In the above diagram P is the proportional limit or it is also known as the limit of proportionality. Stress up to this point is known as proportional limit stress.
According to Hook’s law of proportionality can be defined between point OP. The OP is a straight line which shows the Hook’s law of stress-strain followed up to point P.
Elastic Limit
It is the limiting value of stress up to which the material is perfectly elastic. From the strain stress curve, point E is the elastic limit point. The material gets back to its original position if it is unloaded before crossing point E. That’s why the material is perfectly elastic up to point E.
Yield Stress Point
It is defined as the stress after which material extension takes place more quickly with no or little increase in load. The Y is the yield point on the graph and the stress with this point is called yield stress.
Ultimate Stress Point
It is the ultimate stress point where the maximum strength that the material has to handle stress before breaking. It is also defined as the ultimate stress to the peak point on the stress-strain graph. U is the ultimate stress point on the graph. After U material cannot handle any stress.
Point of Rupture
The point of rupture or breaking point or breaking stress is where the strength of material breaks. In this graph, X is the point of rupture or breaking the stress point.
This is the information about the strain stress curve. We explain the stress and strain diagram.
🔔We hope this information will help you. For more new information click on the notification button and get regular updates from Unbox Factory.
Now if you find this information helpful, share it with your friends, family, and colleagues.
If you like this post, let us know by comment below, if you want to add-on information about this topic, comment the information. We will consider the information if it is relevant.
Thank you for reading.