Contents
- 1 About Venturi Meter
- 1.1 Bernoulli’s Principle
- 1.2 Inside Venturimeter
- 1.3 Converging Section
- 1.4 Cylindrical Throat
- 1.5 Diverging Section
- 1.6 Why the Divergent angle has a limitation?
- 1.7 Differential Manometer and Pressure Gauge
- 1.8 How does it work?
- 1.9 Bernoulli’s Equation
- 1.10 How to find “h” by using a differential U-Tube Manometer?
- 1.11 Where it is used?
- 1.12 Advantages of Venturimeter
- 1.13 Disadvantage
About Venturi Meter
Venturi meter is used to measure the flow rate of fluid via a pipe. It is an application of Bernoulli’s equation. The Venturi Meter principle works on Bernoulli equation like velocity is increase if the pressure decreases. Venturi Meter principle is developed by G.B. Venturi in 1797 but it is first considered with the help of C. Herschel in 1887. The principle states that when the cross-sectional area of the flow is reduced the pressure difference is created between different areas of flow and it helps to measure the difference in pressure. This pressure difference helps to measure the discharge inflow.
Bernoulli’s Principle
The increase in the velocity of the fluid its pressure decreases (or) decreases the fluid potential energy. As decreasing the fluid pressure in the area where flow velocity increases are called the Bernoulli Effect.
Inside Venturimeter
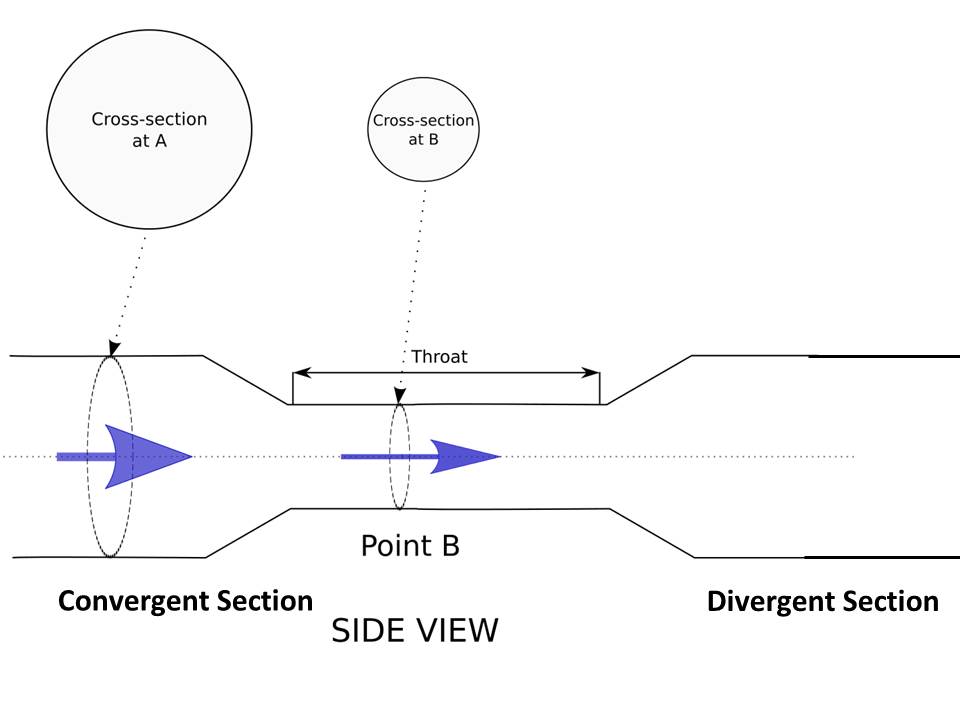
The Venturi meter has a very simple construction and has parts shown in the below image and these parts are arranged systematic order for proper operation and these inlet sections called the converging cone, cylindrical throat, and diverging cone.
Converging Section
In this region, the cross-section emerges into a conical shape for connectivity with the throat region. The converging part is attached to the inlet pipe and the cross-sectional area decreases from beginning to end. On the one side, it is attached to the inlet and on another side, it is attached to the cylindrical throat. The angle of convergence is 20-22 degree and length is 2.7(D-d). the D is the diameter of the inlet section and d is the diameter of the throat. As the decrease in a cross-sectional area the fluid moves fast and the static pressure decreases. The converging area has a maximum cone angle and it is limited to avoid venacontracta as the flow area will be minimum at the throat.
Read Also: What is Francis Turbine?Cylindrical Throat
The cylindrical throat is the middle part of venturimeter and it has the lowest cross-sectional area. Length is equal to the diameter of the throat. Normally the diameter of the throat is ¼ to ¾ diameter of the inlet pipe and mostly it is ½ diameter of the pipe. The diameter of the throat remains the same for its length. The diameter of the throat cannot reduce to its minimum suitable value and if the cross-sectional area decreases velocity increase and pressure decreases. The decrease in pressure goes below the vapor pressure and it results in cavitation. To solve the cavitation, issue the limit the value of diameter.
Diverging Section
The diverging section is the last part of the device. It is attached with an outlet pipe on one side. The diameter of the section is increasing and has an angle of 5 to 15 degree. Diverging angle is less than the converging angle as its length of a diverging cone and it is larger than the converging cone. The reason of small diverging angle is to avoid the flow separation from walls and prevents the formation of eddies as the flow separation and eddies will result in a large amount of loss in energy. And for avoiding this issue the proper angle of converging and diverging should maintain.
Why the Divergent angle has a limitation?
- For reducing adverse pressure gradient and reverse flow like unsteady flow.
- Preventing the flow separation as it causes the frictional drag.
- For avoiding the head loss and cavitation effect.
Differential Manometer and Pressure Gauge
The differential manometer is used to measure the pressure in the flow via the pipe and it is mounted between the inlet pipe and throat. The pressure gauges can be used instead of a differential manometer for measuring the pressure and different sections. It is mounted at the inlet and throat of the venturi meter. This diverging section is not used for measuring the discharge at this section flow separation may occur. As the fluid flow from venturi meter, the pressure difference is to create and it is measured by the differential manometer.
How does it work?
The working of the venturi meter is so simple. As explained above it works on the principle of Bernoulli’s equation like increasing in velocity the pressure is decreased. This same principle is also applicable here. In the venturi meter, the cross-section area of the throat is smaller than the cross-section area of the inlet pipe and due to this the velocity of flow is higher than the inlet section and it happens according to the continuity equation. Increasing in the velocity of flow at the throat will result in a decrease in pressure and due to this there is a pressure difference is developed between the inlet and throat of venturi meter. This developed difference is measured by differential manometer between the inlet section and throat or by two separate gauges at inlet and throat. The two different pressure at two different sections can easily measure the flow rate through the pipe.
The working of the venturi meter is described below.
- It works on Bernoulli’s principle. And the velocity increases the pressure decreases.
- And the convergent region as the area and pressure decrease the velocity increases and a favorable pressure gradient-like (dp/dx)<0.
- At the throat region area and pressure are constant and the velocity is also constant and the pressure gradient is zero. (dp/dx)=0
- A decrease in the pressure in between inlet and throat is measured with the help of a differential manometer.
- The value of the height of mercury in the manometer is obtained from the difference of pressure heads and it is used to calculate discharge by using Bernoulli’s equation.
- And the cone angle of the divergent region is limited to 5 to 7o the reverse flow is eradicated and the pressure gradient is adverse.
Bernoulli’s Equation
The venturi meter is used to obtain the pressure difference only and the discharge rate is obtained by using Bernoulli’s equation.
Guess the convergent region section 1 and throat region section 2.
d1= diameter at inlet
P1= Pressure at inlet
V1= velocity at inlet
A1= Area at inlet
Also
d2= diameter at throat
V2= velocity at throat
P2= pressure at throat
A2= Area at throat
Now applying Bernoulli’s equation on section 1&2
(P1/)+(V12/2g)+Z1=(P2/ρg)+(V22/2g)+Z2
For horizontal pipe Z1=Z2
(P1-P2)/ ρg= (V22 – V12)/2g
A difference of pressure head is measured in ‘h’
As h=(P1-P2)/ ρg
h=(V22-V12)/2g
After applying the continuity equation at 1 & 2
A1V1=A2V2
V1=A2V2/A1
Substituting this value of v1 in the equation
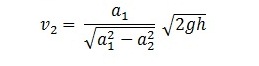
Discharge
Q= A2V2
Now substitute the value of v2 in the above equation
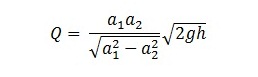
Here Q is the theoretical discharge under ideal condition. The actual discharge will be less than the theoretical discharge. The formula for actual discharge is
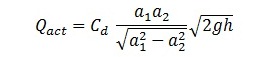
h=(V22/2g) [(A12 – A22) / A12]
For discharge
Q=A1V1=A2h
The above expression is for ideal cases and known as Theoretical discharge.
The actual discharge is less than Theoretical discharge.
Cd is coefficient of venturi meter and always less than 1 (i.e., Cd<1)
How to find “h” by using a differential U-Tube Manometer?
It is depending on flowing fluid and manometer liquid is an expression for “h” and it is differing and given by differential U-Tube manometer.
- If the liquid in the manometer is heavier than the flowing fluid in the pipe.
h= x [(Sh/S0)-1]
- If the liquid in the manometer is heavier than the flowing fluid in the pipe.
h= x [(1-(SL/S0)]
In this equation
S0 = specific gravity of flowing fluid
SL = Specific gravity of the lighter liquid
Sh = Specific gravity of a heavier liquid
X = difference of liquid columns in U – Tube
Where it is used?
Venturi meter is used to measure the discharge inflow through pipes.
In medical applications, it is used to measure the rate of flow in the arteries.
Venturi meter is used in industrial applications like gas, liquids, oil where the pressure loss should avoid.
It is also capable of measuring the discharge of fluid with having slurry or dirt particles as it has smooth design.
Advantages of Venturimeter
- The venturi meter has fewer losses and high accuracy.
- Venturimeter has a high coefficient of discharge.
- It is easy to operate.
- It is easy to install in any direction between pipe flow like horizontal, vertical and inclined.
- Venturi meter has a high accuracy rate compared to other devices like orifice meter, pilot tube, and nozzles.
Disadvantage
It has some disadvantages too like high initial cost as the calculation is complicated.
It is not suitable for a small diameter size pipe.
Venturi meter is difficult to maintain and to inspect.
The initial cost of the venturi meter is high.
This is the information about Venturi Pump and Venturi pump working.
🔔We hope this information will help you. For more new information click on the notification button and get regular updates from Unbox Factory.
Now if you find this information helpful, share it with your friends, family, and colleagues.
If you like this post, let us know by comment below, if you want to add-on information about this topic, comment the information. We will consider the information if it is relevant.
Thank you for reading.